Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Nvidia Rubin CPX GPU
3. Artificial Intelligence Infrastructure
4. AI Stocks
5. Conclusion
While Wall Street's focused on OpenAI's $100 billion deals and Trump's tariffs and trade war with China, Nvidia quietly announced a chip that's about to change the entire AI market. So in this video, I'll put you ahead of every Wall Street analyst by explaining this new chip, what it means for every AI data center, and which stocks could win big as a result. Your time is valuable, so let's get right into it.
First things first, I'm not here to hold you hostage, so here's what I'll cover in this video. India's insane new Rubin CPX GPU, what investors need to know about this chip's purpose, its design and performance, how it will fundamentally change AI infrastructure as we know it, and of course, which stocks I'm buying as a result. There's a ton to talk about. So let's dive right into the chip itself.
A few weeks ago at the AI Infra Summit, Nvidia announced a GPU called the Rubin CPX, a new kind of GPU focused on accelerating massive context inference. Let's break down what that actually means. There are three main phases to generative AI today. Training, post-training, and inference. Training is where an AI model learns structures, patterns, and relationships from massive amounts of example data.
Today's top-of-the-line frontier models, like OpenAI's GPT-5, Google Gemini, or Claude by Anthropic, are trained on all of the data on the entire open internet, using tens of thousands of GPUs working in parallel, connected by highly specialized networking equipment. This training is where the AI model gets aligned and fine-tuned for specific tasks using techniques like reinforcement learning with human feedback to produce even better final outputs.

This is also where guardrails get implemented, not just to stop biased or unsafe outputs, but to keep the AI on the task at hand, so that it doesn't waste tokens on tasks that won't generate revenue. For example, imagine if Netflix or Apple TV had an AI agent that curates content for you. question about politics or religion, it shouldn't respond with a political or religious answer.
Not just because you might disagree with the response, but because that response costs tokens to generate, but it doesn't get you to engage with the content. So instead, that AI agent should be given a guard rail that says if the user asks a political or religious question, recommend content that might answer it instead of answering it yourself. That one little tweak could be the difference between losing money and making money on this AI agent, and it happens during post-training.
Post-training is less compute-intensive than training, but it still takes some specialized hardware and software to turn data labels and human feedback into updated weights for the AI model. The third phase for generative AI is inference. Inference is where an AI model gets a prompt from a user and generates a response, like answering a question, generating a video, or compiling code, one token at a time.

But where training needs a ton of compute, inference needs low latency and lower costs per token. Said another way, training is all about having the compute power to build the best AI model, while inference is all about having the network speed to serve the most users or prompts per second.
That's why hyperscalers like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Meta platforms all have their own custom chips for inference while they use Nvidia's much more powerful, but much more expensive GPUs for model training. Not because these chips compete, but because they do fundamentally different things in the first place.
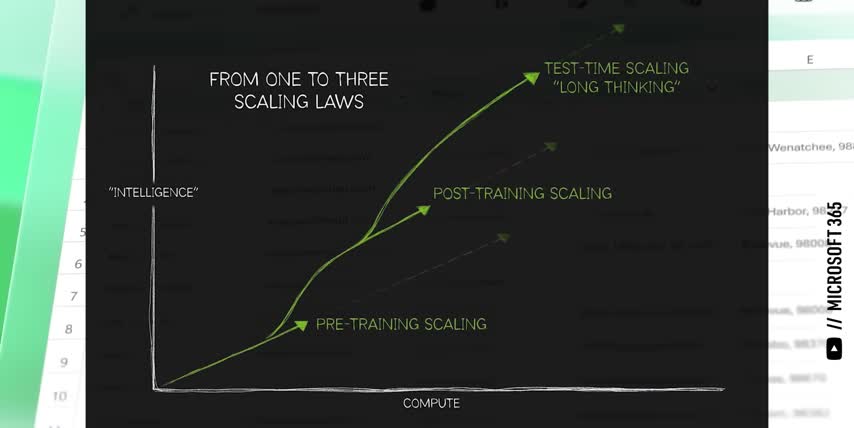
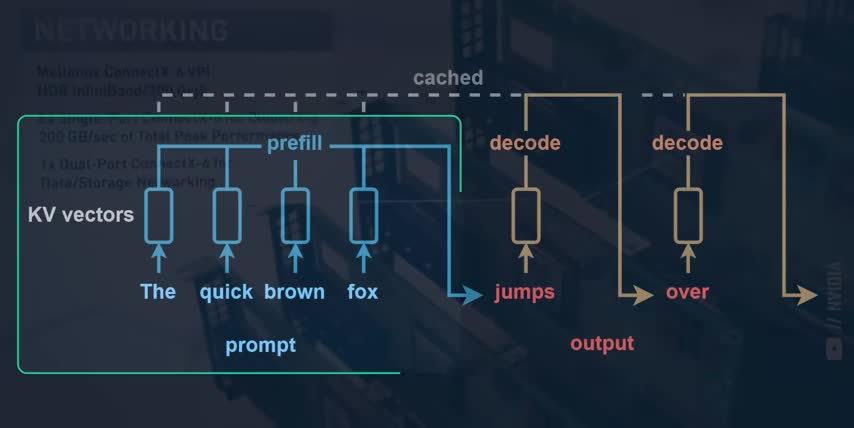
That's also why OpenAI signed multiple $100 billion deals not just with Nvidia, but also with AMD to use their GPUs for inference, and with Broadcom to build their own custom inference chips And this is where Nvidia new Rubin CPX GPU comes in It turns out that inference itself is broken down into two very different steps called Pre and Decode The Pre phase takes the entire input prompt converts it into tokens, runs them through the model, computes the results for every token, which are called key value pairs, and stores those KV pairs in the chip's memory.

Today, input prompts can be millions of tokens long, as people attach multiple PDFs, videos, or even entire code bases to their prompt. For example, Google Gemini 1.5 Pro has a context window of up to 2 million tokens, which is just enough to drop in every Harry Potter book and every Lord of the Rings book put together. You know, for science. Nvidia's Rubin CPX chip is designed for this kind of massive context inference.
It has a ton of compute power to process millions of tokens in parallel, but lower cost, lower bandwidth memory since that's not needed for this part of inference. The second phase of inference is called decode, which is where the chip retrieves all those key value pairs, calculates the next token and its key value pair, adds that to the sequence, and then repeats this process until it finishes generating the entire answer.
But while the pre-fill step takes a ton of compute power to calculate the key value pairs for millions of input tokens, this decode step needs a lot more memory to read them all in, but it needs lot less compute to generate the next token one token at a time. So just like training and inference need totally different kinds of chips, so do the two parts of inference itself, which fundamentally changes how every company will invest in their AI infrastructure going forward.
This is why I think Nvidia's Rubin CPX GPU is such a big deal. This is why it's so important to understand the science behind the stocks, and this is why one of the best investments you can make to get ahead is understanding AI. That's where Outskill comes in, the sponsor of this video. Outskill is the world's first AI-focused education platform and they're hosting a two-day AI training to take you from beginner to advanced AI professional this Saturday and Sunday.
And they're giving the first 1,000 people who sign up with my link a free seat. Whether you work in tech or finance, sales or HR, you'll learn 10 of the most powerful AI tools like Gemini and Grok, best practices for prompting AI and using AI agents and even how to automate workflows without any coding. You'll also get free access to OutSkill's exclusive community and learning dashboard to keep growing alongside other AI professionals.
No wonder over 10 million people from all over the world have already attended, and the limited slots for this one are filling up faster than ever. This is a great way to gain a competitive advantage with AI, get a serious head start for 2026, and understand the science behind the stocks, so make sure to register for your free seat with my link below today. Alright so the two phases of inference have very different hardware requirements.

Prefill takes a ton of compute, but can get away with much slower memory, while decode takes tons of memory bandwidth but nowhere near as much compute.
And the difference in prefill inference performance between Nvidia's Rubin CPX GPU and the standard Rubin GPU will be massive, up to 4 times the compute per dollar, less than half the memory costs since it doesn't needs specialized high bandwidth memory, three times the throughput per GPU, and up to 90 cents per GPU saved every single hour depending on electricity prices, which is one of the biggest costs of operating a data center.
As a result, the NVIDIA Rubin CPX could provide 30 to 50 times the return on investment for pre-fill inference over the standard Rubin 200 GPU.
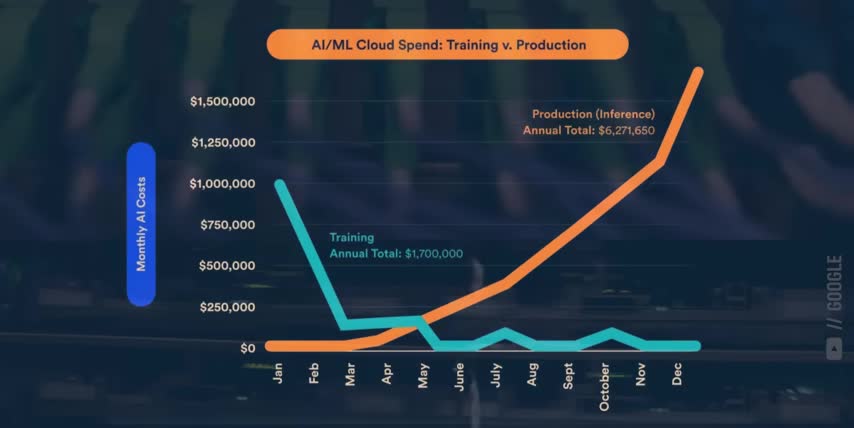
That's a huge deal because inference accounts for 80 to 90 percent of the total costs for a given model since training only happens a handful of times while inference happens at huge scales around the clock across millions of users and applications Now here the part that put you ahead of every Wall Street analyst covering AI infrastructure It not just about this one GPU The global AI data center market is currently expected to roughly 9x in size over the next nine years, which would be a 27% compound annual growth rate through 2034.
Or they can make another chip optimized for reinforcement learning and tuning models based on feedback that runs continuously, which will blur the lines between training and inference altogether or what if amd makes different ai chiplets for processing text audio video and code so their customers can choose the right mix of chiplets based on their workloads that they support not just in data centers but also in ai pcs and just like deep seek r1 kicked off the race for ai reasoning i think nvidia's ruben cpx will start a race for hyper specialized ai chips each with their own power cooling memory and networking requirements.
So every stock I'm about to highlight benefits big time from a future where there are many kinds of specialized AI chips. And if you feel I've earned it, consider sharing this post with others. Thanks and with that out of the way, let's talk AI stocks.

The Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, ticker symbol TSM, is the only foundry on earth advanced enough to make chips for NVIDIA, AMD, Broadcom, Apple, and all of the custom AI chips for hyperscalers like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta platforms. As demand for inference grows, demand for chips to power it grows even faster, since data center infrastructure is planned out years in advance.
So as TSMC's customers start creating more specialized chips for the different phases of AI we just discussed, like pre-fill, decode, and fine-tuning, there will be even more chip designs and higher demand for wafers, which translates to more volume for TSMC's most advanced and most profitable nodes. On top of that, more advanced chips require more specialized packaging techniques to get the GPUs, memory, and networking chiplets close enough together and connected at ultra-high bandwidths.
Not only is TSMC the market leader by far when it comes to advanced packaging, it's also a main driver for their margins. Bottom line, the more demand there is for different advanced AI chip designs, the more TSMC can charge for their supply, making TSM a great stock to get rich without getting lucky over the course of the AI era.

Like I said earlier, the Nvidia Rubin CPX could provide 30 to 50 times the return on investment over the standard Rubin 200 GPU, but the trade-off is that this chip is only for the pre-fill phase of inference, as opposed to being a general chip that's useful for many kinds of workloads. So the next most obvious bet is on the hyperscalers themselves.
Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, who have enough total workload demand to deploy, power, and coordinate these specialized chips at massive scales, and then pass the cost savings onto their customers in a way that smaller competitors might not be able to do.
And right behind them are companies like CoreWeave and Nebius, who build and operate high cloud infrastructure optimized for massive language models generative AI and deep learning these companies deploy the latest gpu and accelerator hardware which will include any phase optimized chips to give their customers the kinds of speed scalability and cost efficiency they couldn't get if they built their own ai infrastructure between the two i personally prefer coreweave because they're nvidia's biggest public investment representing around 90 of the company's stock portfolio there's also companies that connect these chips together like arista networks ticker symbol a net arista designs specialized switches network control software and management tools to build huge reliable and fast networks at large scales arista networks also works closely with broadcom ticker symbol avgo who just partnered with openai to build their custom inference chips arista's switches and software are actually built around broadcom's ultra-fast tomahawk switch chips which is how they're able to stay ahead of the growing networking needs for ai today so as new kinds of phase optimized chips enter the ai market companies like broadcom and arista networks will be the ones connecting them together to handle highly parallel workloads at incredibly high speeds but all these specialized ai chips are useless if you can't power them or keep them cool which is why the last stock on my list is vertive holdings ticker symbol vrt one thing that i keep pounding the table on is that around 80 to 90 percent of all data center server racks are still air cooled today but industry estimates suggest that up to 80 percent of them will eventually transition to direct to chip liquid cooling directed chip liquid cooling is where a heat conductive copper plate is mounted directly to the chip that plate is then connected to two pipes one pipe brings in cool water to absorb the heat and the other pipe moves the hot water away.

Liquid cooling is up to 3,000 times more efficient than air cooling, making it an obvious investment for any data center looking to power AI workloads. As a result, the data center liquid cooling market is expected to almost 5x in size over the next 8 years, which would be a compound annual growth rate of 21% through 2033.
And if you watched my recent videos, you know that Nvidia‘s Blackwell, blackwell ultra and rubin systems require liquid cooling so i think this transition from air cooling to liquid will be much bigger than most analysts expect especially if more new chips like the rubin cpx are on the way well vertive holdings makes power and thermal management systems for data centers for example their liber liquid cooling systems focus on high density server deployments like massive gpu clusters for ai training and inference vertive supplies critical cooling solutions to all three hyperscalers amazon web services google cloud and microsoft azure vertive also supplies them with core power systems like their libra e-xl a high capacity uninterruptible power supply designed specifically for hyperscale and cloud facilities it supplies huge amounts of energy at very high efficiencies making vertive a solid stock to buy as more kinds of chips need custom cooling and power solutions hopefully this video helped you understand nvidia's insane new Rubin CPX GPU, how it will fundamentally change AI infrastructure as we know it, and the kinds of stocks that will win big as a result.

Because understanding a company's products, and not just their profits, is a great way to get rich without getting lucky. And if you want to see what else I'm investing in to get rich without getting lucky, check out this post next. Either way, thanks for reading and until next time, this is TickerSymbol: YOU. My name is Alex reminding you that the best investment you can make is in you.
Key Takeaways
- Nvidia's Rubin CPX GPU is designed for massive context inference and will change the AI infrastructure landscape.
- The global AI data center market is expected to grow at a 27% compound annual growth rate through 2034.
- TSMC is the only foundry advanced enough to make chips for NVIDIA, AMD, Broadcom, Apple, and custom AI chips for hyperscalers.
- Specialized chips for different phases of AI, like pre-fill, decode, and fine-tuning, will drive demand for more chip designs and higher demand for wafers.
- Companies like CoreWeave, Nebius, Arista Networks, and Broadcom will benefit from the growing demand for specialized AI chips and infrastructure.
Checkout our YouTube Channel
Get the latest videos and industry deep dives as we check out the science behind the stocks.